“She habitually engages in psychological projection. She has caused me to be compelled under threat of arrest and prosecution for failure to appear to attend court on her frivolous lawsuits 25 times. Yes! Twenty-five times. The frivolous prosecutions started in 2011, and they are still raging. I have been cited back to court on her application for a new restraining order on the 12th and a criminal warrant for cyberstalking on the 17th of this month. She has tried so many times to have me jailed I have lost count.”
—Larry Smith, author of BuncyBlawg.com (2014)
The quotation above is an excerpt from an email sent to the creator of “Neighbors from Hell” on ABC’s 20/20. The Feb. 8 email was a sorely persecuted man’s response to being fingered on Facebook as a candidate for the series by his neighbor, Marty Tackitt-Grist, who has forced him to appear before judges nearly 30 times in the span of a few years to answer “two restraining orders, three show-cause orders, two cyberstalking arrests, and a failure-to-appear arrest and jailing despite faxes from two doctors that I was too crippled, disabled, and suffering from herniated discs to be able to attend court.”
 Here’s the reply the email elicited from ABC’s Bob Borzotta: “Hi Larry, I don’t seem to have heard further from her. Sounds like quite a situation….” Cursory validations like this one are the closest thing to solace that victims of chronic legal abuses can expect.
Here’s the reply the email elicited from ABC’s Bob Borzotta: “Hi Larry, I don’t seem to have heard further from her. Sounds like quite a situation….” Cursory validations like this one are the closest thing to solace that victims of chronic legal abuses can expect.
Concern shown by the police and courts to complaints from attention-seekers can make them feel like celebrities. Random wild accusations are all it takes for the perennial extra in life to realize his or her name in lights.
Not unpredictably, the thrill is addictive.
I think I first heard from Larry, the author of BuncyBlawg.com, in 2013—or maybe it was 2012. In the artificial limbo created by “high-conflict” people like the one he describes in the epigraph, temporal guideposts are few and far between. A target like Larry can find him- or herself living the same day over and over for years, because s/he’s unable to plan, look forward to anything, or even enjoy a moment’s tranquility.
 The target of a high-conflict person is perpetually on the defensive, trying to recover his or her former life from the unrelenting grasp of a crank with an extreme (and often pathological) investment in eroding that life for self-aggrandizement and -gratification.
The target of a high-conflict person is perpetually on the defensive, trying to recover his or her former life from the unrelenting grasp of a crank with an extreme (and often pathological) investment in eroding that life for self-aggrandizement and -gratification.
Among Larry’s neighbor’s published allegations are that he’s a disbarred attorney who “embezzled from his clients” and a textbook psychopath, that he has “barked like a dog for hours” to provoke another neighbor’s (imaginary) dog to howl at her, that he has called her names, that he has enlisted “mentally challenged adults” to harass her while shopping, that he has cyberstalked her, that he has “hacked into phones” and computers, that he has tried to cause her (and “many others”) to lose their jobs by “reporting false information,” that he has made false complaints about her “to every city, state, and county service,” that he sends her mail “constantly,” and that he has “mooned” her neighbors and friends.
 The ease with which a restraining order is obtained encourages outrageous defamations like these (Larry’s neighbor has sworn out two). Once a high-conflict person sees how readily any fantastical allegation can be put over on the police and courts, s/he’s inspired to unleash his or her imagination. That piece of paper not only licenses lies; it motivates them.
The ease with which a restraining order is obtained encourages outrageous defamations like these (Larry’s neighbor has sworn out two). Once a high-conflict person sees how readily any fantastical allegation can be put over on the police and courts, s/he’s inspired to unleash his or her imagination. That piece of paper not only licenses lies; it motivates them.
Larry’s a quiet guy with a degenerative spinal disorder who’s been progressively going deaf for 25 years. He lives for his three toy poodles and watches birds. “I grew up,” he says, “in a little Arcadian valley here in western North Carolina with the nicest people, mostly farmers; and I guess my youth just left me naïve about some people. I always saw the good in them.” Larry began practicing law in 1973 in Asheville but voluntarily withdrew from the profession in 1986, because he was disgusted by the corruption—and the irony of having his retirement years fouled by that corruption isn’t lost on him.
You might guess his accuser’s motive to be that of a woman scorned, but Larry’s association with her has never exceeded that of the usual neighborly sort. He reports, however, that she has alleged in court that he covets her and nurses unrequited longings and desires.
Compare the details of the infamous David Letterman case, and see if you don’t note the same correspondence Larry has.
 That’s the horror that only the objects of high-conflict people’s fixations understand. Stalkers and “secret admirers” procure restraining orders to get attention and embed themselves in other’s lives—like shrapnel.
That’s the horror that only the objects of high-conflict people’s fixations understand. Stalkers and “secret admirers” procure restraining orders to get attention and embed themselves in other’s lives—like shrapnel.
This writer has been in and out of court for eight years subsequent to encountering a stranger standing outside of his residence one day…and naïvely welcoming her. One respondent to this blog reported having had a restraining order issued against her by a man she sometimes encountered by her home who always made a point of noticing her but with whom she’d never exchanged a single word.
It isn’t only intimates and exes who lie to subject targets to public humiliation and punishment. Sometimes it’s lurkers and passers-by, covert observers who peer between fence slats and entertain fantasies—or, as in Larry’s case, a neighbor who feels s/he’s been slighted or wronged according to metrics that only make sense to him or her.
Larry thinks the unilateral feud that has exploded the last several years of his life originates with his complaining about cats his neighbor housed, after they savaged the fledgling birds that have always been his springtime joy to watch.
For 25 years I have lived on this street with lovely people. We always got along, although one or two you had to watch. During most of that 25 years, there have been three different owners of the house across the street. The other two we dearly loved. The last one, the incarnation of purest evil, moved here in 2005. She was a divorcée who volunteered that her divorce was especially nasty, the first red flag which I foolishly disregarded: She constantly badmouthed her ex. For the first few years, we were friends, but as time went by she became an almost insufferable mooch and just way too friendly, expecting more attention from her neighbors, and from us, than we wanted to give. Sometime in early 2011, I left her a voicemail and told her I didn’t want to be close friends with her anymore. She was a hoverer, she manipulated, she was a narcissist. And the message meant that I did not want to be called on to mow her lawn anymore, or help her trim her trees, or lend her tools, or watch her pet while she was gone, or help her move heavy loads like furniture, or listen to her constant whining. I just wanted to cool it with her.
 In the spring of 2011, she had been converting her home to a sort of boarding house and brought in tenants, and [between] them they had two cats that constantly prowled, especially the tenant’s. What became very irksome to me was the tenant’s cat creeping into our yard and killing our baby birds, which we always looked forward to in the spring. And the minute I brought it up with her, she pitched a fit, and so did the tenant. So for the first two months of baby bird season, [their] cats killed all our fledglings and the mother songbirds—wrens, cardinals, robins, mockingbirds, towhees, mourning doves, even the hummingbirds, just wiped them out. I finally got in touch with our Animal Services officers, but by that time bird season was over with, and you know something, [she] began going about telling neighbors that I was a disbarred lawyer (a particularly nasty slander). One thing led to another, and finally the tenant with the marauding cat moved away, but the irreparable damage was done, and all through the summer I had been warned by other neighbors that the neighbor from hell was plotting revenge.
In the spring of 2011, she had been converting her home to a sort of boarding house and brought in tenants, and [between] them they had two cats that constantly prowled, especially the tenant’s. What became very irksome to me was the tenant’s cat creeping into our yard and killing our baby birds, which we always looked forward to in the spring. And the minute I brought it up with her, she pitched a fit, and so did the tenant. So for the first two months of baby bird season, [their] cats killed all our fledglings and the mother songbirds—wrens, cardinals, robins, mockingbirds, towhees, mourning doves, even the hummingbirds, just wiped them out. I finally got in touch with our Animal Services officers, but by that time bird season was over with, and you know something, [she] began going about telling neighbors that I was a disbarred lawyer (a particularly nasty slander). One thing led to another, and finally the tenant with the marauding cat moved away, but the irreparable damage was done, and all through the summer I had been warned by other neighbors that the neighbor from hell was plotting revenge.
I went to her one day and asked her if there was anything I could do to make it so we could at least drop all the nasty hostilities. She exploded. Next thing I knew, she had three police cruisers here with a false tale that I was “harassing” her and calling her names. This was no surprise, because early on I learned not to believe a thing she said because she just made up the most unbelievable tales about her personal crises. One of the five cops who came spoke with me in the yard, and I thought this would all blow over, but in a few days a process server was banging on the door with papers to serve me. I met him in a commercial parking lot nearby and accepted the lawsuit, an application for a restraining order, a TRO, and, well, a great big wad of lies. It was a shocker. And little did I know that the very day I received this horse-choking wad of papers, at around 10:15 a.m., [she] was back in the courthouse filing another affidavit to have me ordered to show cause why I should not be jailed for contempt. In other words, before I even had notice of the TRO, she was trying to have me jailed for violating it. That’s just how damn mean that woman is.
High-conflict people are driven by a lust to punish—any slight is a provocation to go to war—and their craving for attention can be boundless. Judicial process rewards both.
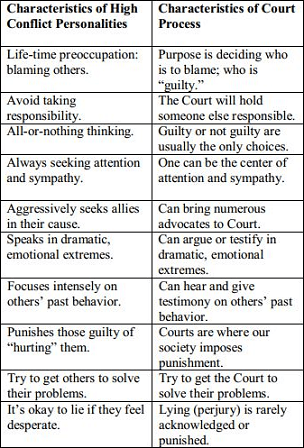
This table, prepared by attorneys Beth E. Maultsby and Kathryn Flowers Samler for the 2013 State Bar of Texas Annual Advanced Family Law Course, shows how high-conflict people and court process are an exquisitely infernal fit. Its authors’ characterization of high-conflict people’s willingness to lie (“if they feel desperate”) is generous. Many lie both on impulse or reflex and with deliberate cunning, though their chain of reasoning may be utterly bizarre.
Restraining orders are easily obtained, particularly by histrionic women. Once petitioners—especially high-conflict petitioners—realize how readily the state’s prepared to credit any evil nonsense they sputter or spew, and once they realize, too, the social hay they can make out of reporting to others that they “had to get a restraining order” (a five-minute affair), they can become accusation junkies.
Larry has responded in the most reasonable way he can to his situation. He’s voiced his outrage and continues to in a blog, and the vehemence of his criticisms might lead some who don’t know Larry to dismiss him as a crank. If you consulted his blog, you’d see it’s fairly rawboned and hardly suggests the craftsmanship of a technical wizard who can hack email accounts and remotely eavesdrop on telephone conversations. What the commentaries there suggest, rather, is the moral umbrage of an intelligent man who’s been acutely, even traumatically sensitized to injustice.
Here’s the diabolical beauty of our restraining order process. Judges accept allegations of abuse at face value and don’t scruple about incising them on the public records of those accused. They furthermore expect those who are defamed to pacifically tolerate public allegations that may have no relationship with reality whatever or may be the opposite of the truth, may be scandalous, and may destroy them socially, professionally, and psychologically. Judges, besides, make the accused vulnerable to any further allegations their accusers may hanker to concoct, which can land them in jail and give them criminal records. And finally judges react with disgust and contempt when the accused ventilate anger, which they may even be punished for doing.
Judicial reasoning apparently runs something like this: If you’re angry about false allegations, then they weren’t false; if you’re not angry about false allegations, then they weren’t false.
Larry’s been jailed, Larry’s been reported to the police a dozen times or more, an officer has rested the laser sight of her sidearm on him through the window of his residence, and the number of times he’s been summoned to court is closing on 30.
The allegations against him have been false. How angry should he be?
Copyright © 2014 RestrainingOrderAbuse.com
 Judge Stump quickly signed the order, and the judge and mamma hustled Linda into a hospital, telling her it was for an appendicitis operation. Linda was then sterilized without her knowledge. Two years later, Linda married a Leo Sparkman and discovered that she had been sterilized without her knowledge. The Sparkmans proceeded to sue mamma, mamma’s attorney, the doctors, the hospital, and Judge Stump, alleging a half-dozen constitutional violations.
Judge Stump quickly signed the order, and the judge and mamma hustled Linda into a hospital, telling her it was for an appendicitis operation. Linda was then sterilized without her knowledge. Two years later, Linda married a Leo Sparkman and discovered that she had been sterilized without her knowledge. The Sparkmans proceeded to sue mamma, mamma’s attorney, the doctors, the hospital, and Judge Stump, alleging a half-dozen constitutional violations.
 People falsely alleged to be abusers on restraining order petitions, particularly men, are treated like brutes, sex offenders, and scum by officers of the court and its staff, besides by authorities and any number of others. Some report their own relatives remain suspicious—often based merely on finger-pointing that’s validated by some judge in a few-minute procedure (and that’s when relatives aren’t the ones making the false allegations).
People falsely alleged to be abusers on restraining order petitions, particularly men, are treated like brutes, sex offenders, and scum by officers of the court and its staff, besides by authorities and any number of others. Some report their own relatives remain suspicious—often based merely on finger-pointing that’s validated by some judge in a few-minute procedure (and that’s when relatives aren’t the ones making the false allegations). So…slanders and libels made by abuse of court process aren’t actionable, slanders and libels that completely sunder the lives of the wrongly accused, who can’t even get them expunged from their records to simply reset their fractured lives to zero.
So…slanders and libels made by abuse of court process aren’t actionable, slanders and libels that completely sunder the lives of the wrongly accused, who can’t even get them expunged from their records to simply reset their fractured lives to zero.

 Buncombe County, North Carolina, where
Buncombe County, North Carolina, where  She says he’s “barked like a dog” at her, recruited “mentally challenged adults” to harass her while shopping, and mooned her friends. She says he’s cyberstalked her, too, besides hacking into her phone and computer.
She says he’s “barked like a dog” at her, recruited “mentally challenged adults” to harass her while shopping, and mooned her friends. She says he’s cyberstalked her, too, besides hacking into her phone and computer.
 My son’s girlfriend…filed a domestic abuse CPO [civil protection order] against my son, again telling him that he shouldn’t have left her. He hasn’t been served yet—they keep missing him. She calls my son constantly, stringing him along with the idea that she “might” let it go. He’s taking her out to eat, giving her money, staying the night with her. Hoping that she’ll let it go. All that and yet two hearing dates for him have come and gone with her showing up at both his hearings asking for a continuance because he hasn’t been served.
My son’s girlfriend…filed a domestic abuse CPO [civil protection order] against my son, again telling him that he shouldn’t have left her. He hasn’t been served yet—they keep missing him. She calls my son constantly, stringing him along with the idea that she “might” let it go. He’s taking her out to eat, giving her money, staying the night with her. Hoping that she’ll let it go. All that and yet two hearing dates for him have come and gone with her showing up at both his hearings asking for a continuance because he hasn’t been served. That includes control of the truth. Some cases of blackmail this author has been informed of were instances of the parties accused knowing something about their accusers that their accusers didn’t want to get around (usually criminal activity). When the guilty parties no longer trusted that coercion would ensure that those who had the goods on them would keep quiet, they filed restraining orders against them alleging abuse, which instantly discredited anything the people they accused might disclose about their activities.
That includes control of the truth. Some cases of blackmail this author has been informed of were instances of the parties accused knowing something about their accusers that their accusers didn’t want to get around (usually criminal activity). When the guilty parties no longer trusted that coercion would ensure that those who had the goods on them would keep quiet, they filed restraining orders against them alleging abuse, which instantly discredited anything the people they accused might disclose about their activities. A recent NPR story reports that dozens of students who’ve been accused of rape are suing their universities. They allege they were denied due process and fair treatment by college investigative committees, that is, that they were “railroaded” (and publicly humiliated and reviled). The basis for a suit alleging civil rights violations, then, might also exist (that is, independent of claims of material privation). Certainly most or all restraining order defendants and many domestic violence defendants are “railroaded” and subjected to public shaming and social rejection unjustly.
A recent NPR story reports that dozens of students who’ve been accused of rape are suing their universities. They allege they were denied due process and fair treatment by college investigative committees, that is, that they were “railroaded” (and publicly humiliated and reviled). The basis for a suit alleging civil rights violations, then, might also exist (that is, independent of claims of material privation). Certainly most or all restraining order defendants and many domestic violence defendants are “railroaded” and subjected to public shaming and social rejection unjustly. Undertaking a venture like coordinating a class action is beyond the resources of this writer, but anyone with the gumption to try and transform words into action is welcome to post a notice here.
Undertaking a venture like coordinating a class action is beyond the resources of this writer, but anyone with the gumption to try and transform words into action is welcome to post a notice here.
 The scales of justice are tipped from the start.
The scales of justice are tipped from the start. The savvy observer will note that suspicion is the motive determiner of liability at all levels. Suspicion informs judicial disposition, subsequent police response to claims of violation, and of course interpretation by third parties, including employers (judges trust accusers, and everyone else trusts judges). Emphatically worthy of remark is that
The savvy observer will note that suspicion is the motive determiner of liability at all levels. Suspicion informs judicial disposition, subsequent police response to claims of violation, and of course interpretation by third parties, including employers (judges trust accusers, and everyone else trusts judges). Emphatically worthy of remark is that  From these concepts, questions immediately present themselves. Are protection orders being utilized in oppressive or unexpected ways? Are the factual scenarios involved similar to what the [legislature] envisioned them to be? Are courts utilizing protection order tools correctly? Are judges issuing ex parte orders that trample upon the rights of innocent people before a hearing is held to determine the validity of specific allegations? Is this area of the law an insufficiently regulated “wild frontier”?
From these concepts, questions immediately present themselves. Are protection orders being utilized in oppressive or unexpected ways? Are the factual scenarios involved similar to what the [legislature] envisioned them to be? Are courts utilizing protection order tools correctly? Are judges issuing ex parte orders that trample upon the rights of innocent people before a hearing is held to determine the validity of specific allegations? Is this area of the law an insufficiently regulated “wild frontier”? While how commonly the process is exploited for ulterior motives is a matter of heated dispute, its availability for abuse is plain. The
While how commonly the process is exploited for ulterior motives is a matter of heated dispute, its availability for abuse is plain. The 
 The news story the epigraph was excerpted from was prompted by a recent murder in Oregon and explores the impotence of restraining orders, in particular to “stop bullets.” Just as shooting sprees inspire reporters to investigate gun legislation, murder victims who had applied for restraining orders that proved worthless inspire reporters to investigate restraining order policies. The presumption, always, is that the law failed.
The news story the epigraph was excerpted from was prompted by a recent murder in Oregon and explores the impotence of restraining orders, in particular to “stop bullets.” Just as shooting sprees inspire reporters to investigate gun legislation, murder victims who had applied for restraining orders that proved worthless inspire reporters to investigate restraining order policies. The presumption, always, is that the law failed.
 “For some people it’s more dangerous [to get a restraining order],” said Kim Larson, director for Marion County District Attorney Victim Assistance Division. “Sometimes it makes people really angry, getting served with a restraining order.”
“For some people it’s more dangerous [to get a restraining order],” said Kim Larson, director for Marion County District Attorney Victim Assistance Division. “Sometimes it makes people really angry, getting served with a restraining order.” My ex-husband’s family just filed their second bogus restraining order against me to overturn custody of our 13-year-old. The first one, three years ago, I spent three months and $25,000 to fight, and got my son back. This one? I promised myself not to fight if they tried again, and I didn’t and lost today in court. They upheld the emergency order of protection and extended a restraining order against me for no contact with my own son for nothing I did at all—for two years. My son wants to be with them, so I’m not fighting. I just don’t want him to grow up thinking I did anything wrong and that’s why they took him from me. I don’t need to lose any more money and get fired from any more jobs trying to fight…. I’m done.
My ex-husband’s family just filed their second bogus restraining order against me to overturn custody of our 13-year-old. The first one, three years ago, I spent three months and $25,000 to fight, and got my son back. This one? I promised myself not to fight if they tried again, and I didn’t and lost today in court. They upheld the emergency order of protection and extended a restraining order against me for no contact with my own son for nothing I did at all—for two years. My son wants to be with them, so I’m not fighting. I just don’t want him to grow up thinking I did anything wrong and that’s why they took him from me. I don’t need to lose any more money and get fired from any more jobs trying to fight…. I’m done. Feminists are encouraged to respond to this mom’s story, whether with sympathy or criticism. The court process she’s a victim of isn’t one this writer condones. Let’s hear from some people who do condone it.
Feminists are encouraged to respond to this mom’s story, whether with sympathy or criticism. The court process she’s a victim of isn’t one this writer condones. Let’s hear from some people who do condone it.
 On 15 March 2009 at 11.07pm: Hi there! How are you? I am lying in my bed and thinking…I miss you and miss having you in my life and I would love to have you back in it…. I do have a lot of issues, I know, and I suppose I am a difficult woman at times…. In the same breath, I could have made the biggest tit out of myself now, because you might have met someone else…. Deep down inside I hope you miss me as much as I miss you! […] I don’t want you to feel that I am pressurising you….
On 15 March 2009 at 11.07pm: Hi there! How are you? I am lying in my bed and thinking…I miss you and miss having you in my life and I would love to have you back in it…. I do have a lot of issues, I know, and I suppose I am a difficult woman at times…. In the same breath, I could have made the biggest tit out of myself now, because you might have met someone else…. Deep down inside I hope you miss me as much as I miss you! […] I don’t want you to feel that I am pressurising you…. A female respondent to the blog brought my attention to the three-year-old story out of Cape Town, South Africa from which the epigraph is excerpted. It’s about a man who was served with a domestic violence restraining order (later revised to a stalking protection order) petitioned by a woman he’d threatened to “un-friend” on Facebook and with whom he’d never had a domestic relationship (he says they had fatefully “kissed once or twice” during a “brief fling”). The order was apparently the tag-team brainchild of this woman, who would be called a stalker according to even the most forgiving standards, and another woman, an attorney the man had dated for six months.
A female respondent to the blog brought my attention to the three-year-old story out of Cape Town, South Africa from which the epigraph is excerpted. It’s about a man who was served with a domestic violence restraining order (later revised to a stalking protection order) petitioned by a woman he’d threatened to “un-friend” on Facebook and with whom he’d never had a domestic relationship (he says they had fatefully “kissed once or twice” during a “brief fling”). The order was apparently the tag-team brainchild of this woman, who would be called a stalker according to even the most forgiving standards, and another woman, an attorney the man had dated for six months.
 Here are two recent headlines that caught my eye: “
Here are two recent headlines that caught my eye: “ Recognize that in these rare instances when perjury statutes are enforced, the motive is political impression management (government face-saving). Everyday claimants who lie to judges are never charged at all, because the victims of their lies (moms, dads,
Recognize that in these rare instances when perjury statutes are enforced, the motive is political impression management (government face-saving). Everyday claimants who lie to judges are never charged at all, because the victims of their lies (moms, dads,  pay them money I didn’t even owe! This person was my babysitter, who is the most manipulative, money hungry witch. I just didn’t know it until now.
pay them money I didn’t even owe! This person was my babysitter, who is the most manipulative, money hungry witch. I just didn’t know it until now.
 Appreciate that the court’s basis for issuing the document capped with the “Warning” pictured above is nothing more than some allegations from the order’s plaintiff, allegations scrawled on a form and typically made orally to a judge in four or five minutes.
Appreciate that the court’s basis for issuing the document capped with the “Warning” pictured above is nothing more than some allegations from the order’s plaintiff, allegations scrawled on a form and typically made orally to a judge in four or five minutes.

 Grant Dossetto has a degree in finance he can’t use.
Grant Dossetto has a degree in finance he can’t use. Though his mother lived to see him earn his degree with honors in 2009, neither of Grant’s parents will ever know that their investment in their son’s success was betrayed or that his professional aspirations were dashed, because they’ve passed away.
Though his mother lived to see him earn his degree with honors in 2009, neither of Grant’s parents will ever know that their investment in their son’s success was betrayed or that his professional aspirations were dashed, because they’ve passed away. In Grant’s home state of Michigan, this qualifies as service. No copy of the order was ever provided to him.
In Grant’s home state of Michigan, this qualifies as service. No copy of the order was ever provided to him. No surprise, Grant has “suffered from severe depression that still surfaces at times now.” His case exemplifies the justice system’s willingness to compound the stresses of real exigencies like family crises with false exigencies like nonexistent danger.
No surprise, Grant has “suffered from severe depression that still surfaces at times now.” His case exemplifies the justice system’s willingness to compound the stresses of real exigencies like family crises with false exigencies like nonexistent danger.

 The judge who issued the 2010 order, James Biernat, Sr., is famous for presiding over the “Comic Book Murder” case. It was big enough to make Dateline and the other true crime outlets. He overturned a guilty conviction from a jury and demanded a retrial. The action was extraordinary, held up on appeal by a split decision. The Macomb prosecutor publically rebuked him as being soft on crime. That made national news. All the cable outlets covered the second trial, which yielded the same result: guilty. He was rebuked by two dozen jurors, three appellate justices, and the prosecutor. It’s funny, if he had just given me a hearing, let alone a second, I truly believe a PPO would never have been issued.
The judge who issued the 2010 order, James Biernat, Sr., is famous for presiding over the “Comic Book Murder” case. It was big enough to make Dateline and the other true crime outlets. He overturned a guilty conviction from a jury and demanded a retrial. The action was extraordinary, held up on appeal by a split decision. The Macomb prosecutor publically rebuked him as being soft on crime. That made national news. All the cable outlets covered the second trial, which yielded the same result: guilty. He was rebuked by two dozen jurors, three appellate justices, and the prosecutor. It’s funny, if he had just given me a hearing, let alone a second, I truly believe a PPO would never have been issued.


 Members of the legislative subcommittee referenced in The Courant article reportedly expect to improve their understanding of the flaws inherent in the restraining order process by taking a field trip. They plan “a ‘ride along’ with the representative of the state marshals on the panel…to learn more about how restraining orders are served.”
Members of the legislative subcommittee referenced in The Courant article reportedly expect to improve their understanding of the flaws inherent in the restraining order process by taking a field trip. They plan “a ‘ride along’ with the representative of the state marshals on the panel…to learn more about how restraining orders are served.”
 It’s often reported by recipients of restraining orders that the cops and constables who serve them recognize they’re stigmatizing.
It’s often reported by recipients of restraining orders that the cops and constables who serve them recognize they’re stigmatizing. “Obscure public records” is how some officers of the court think of restraining orders. In the age of the Internet, there are no such things. Many judges are in their 60s and 70s, however, and scarcely know the first thing about the Internet, let alone Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. They’re still living in the days of mimeographs and microfiche.
“Obscure public records” is how some officers of the court think of restraining orders. In the age of the Internet, there are no such things. Many judges are in their 60s and 70s, however, and scarcely know the first thing about the Internet, let alone Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. They’re still living in the days of mimeographs and microfiche.
 What people should find disturbing about these stories is how feminine false accusers think about lying, including lying about physical and sexual violence (or their threat). They think it’s no big deal—or they don’t think about it at all.
What people should find disturbing about these stories is how feminine false accusers think about lying, including lying about physical and sexual violence (or their threat). They think it’s no big deal—or they don’t think about it at all. Feminine and feminist psychology are due more scrutiny than they receive. I can’t count the number of times I’ve read even sympathetic reporters of false allegations say they recognize that the more urgent problem is (sexual) violence against women—a sentiment that, intentionally or not, motivates false allegations. False accusers aren’t just aided and abetted by this pronouncement of priority; they’re encouraged by it.
Feminine and feminist psychology are due more scrutiny than they receive. I can’t count the number of times I’ve read even sympathetic reporters of false allegations say they recognize that the more urgent problem is (sexual) violence against women—a sentiment that, intentionally or not, motivates false allegations. False accusers aren’t just aided and abetted by this pronouncement of priority; they’re encouraged by it. Here’s the reply the email elicited from ABC’s Bob Borzotta: “Hi Larry, I don’t seem to have heard further from her. Sounds like quite a situation….” Cursory validations like this one are the closest thing to solace that victims of chronic legal abuses can expect.
Here’s the reply the email elicited from ABC’s Bob Borzotta: “Hi Larry, I don’t seem to have heard further from her. Sounds like quite a situation….” Cursory validations like this one are the closest thing to solace that victims of chronic legal abuses can expect. The target of a high-conflict person is perpetually on the defensive, trying to recover his or her former life from the unrelenting grasp of a crank with an extreme (and often pathological) investment in eroding that life for self-aggrandizement and -gratification.
The target of a high-conflict person is perpetually on the defensive, trying to recover his or her former life from the unrelenting grasp of a crank with an extreme (and often pathological) investment in eroding that life for self-aggrandizement and -gratification. The ease with which a restraining order is obtained encourages outrageous defamations like these (Larry’s neighbor has sworn out two). Once a high-conflict person sees how readily
The ease with which a restraining order is obtained encourages outrageous defamations like these (Larry’s neighbor has sworn out two). Once a high-conflict person sees how readily 
 In the spring of 2011, she had been converting her home to a sort of boarding house and brought in tenants, and [between] them they had two cats that constantly prowled, especially the tenant’s. What became very irksome to me was the tenant’s cat creeping into our yard and killing our baby birds, which we always looked forward to in the spring. And the minute I brought it up with her, she pitched a fit, and so did the tenant. So for the first two months of baby bird season, [their] cats killed all our fledglings and the mother songbirds—wrens, cardinals, robins, mockingbirds, towhees, mourning doves, even the hummingbirds, just wiped them out. I finally got in touch with our Animal Services officers, but by that time bird season was over with, and you know something, [she] began going about telling neighbors that I was a disbarred lawyer (a particularly nasty slander). One thing led to another, and finally the tenant with the marauding cat moved away, but the irreparable damage was done, and all through the summer I had been warned by other neighbors that the neighbor from hell was plotting revenge.
In the spring of 2011, she had been converting her home to a sort of boarding house and brought in tenants, and [between] them they had two cats that constantly prowled, especially the tenant’s. What became very irksome to me was the tenant’s cat creeping into our yard and killing our baby birds, which we always looked forward to in the spring. And the minute I brought it up with her, she pitched a fit, and so did the tenant. So for the first two months of baby bird season, [their] cats killed all our fledglings and the mother songbirds—wrens, cardinals, robins, mockingbirds, towhees, mourning doves, even the hummingbirds, just wiped them out. I finally got in touch with our Animal Services officers, but by that time bird season was over with, and you know something, [she] began going about telling neighbors that I was a disbarred lawyer (a particularly nasty slander). One thing led to another, and finally the tenant with the marauding cat moved away, but the irreparable damage was done, and all through the summer I had been warned by other neighbors that the neighbor from hell was plotting revenge.
 Its introduction, at least, was gripping to read: “At what was billed as the first annual international conference on men’s issues, feminists were ruining everything.” I was keen to hear about how the meeting was disrupted by a mob of angry women swinging truncheons.
Its introduction, at least, was gripping to read: “At what was billed as the first annual international conference on men’s issues, feminists were ruining everything.” I was keen to hear about how the meeting was disrupted by a mob of angry women swinging truncheons. I’m sympathetic to men’s plaints about legal mockeries that trash lives, including those of children, so I found the MSNBC coverage offensively yellow-tinged in more senses than one, but I’m not what feminists call an MRA or “men’s rights activist.” I don’t think men need any rights the Constitution doesn’t already promise them. What they need is for their government to recognize and honor those rights. The objection to feminism is that it has induced the state to act in wanton violation of citizens’ civil entitlements—not just men’s, but women’s, too.
I’m sympathetic to men’s plaints about legal mockeries that trash lives, including those of children, so I found the MSNBC coverage offensively yellow-tinged in more senses than one, but I’m not what feminists call an MRA or “men’s rights activist.” I don’t think men need any rights the Constitution doesn’t already promise them. What they need is for their government to recognize and honor those rights. The objection to feminism is that it has induced the state to act in wanton violation of citizens’ civil entitlements—not just men’s, but women’s, too. To illustrate, take the
To illustrate, take the  Women I’ve corresponded with in the three years I’ve maintained this blog have reported being stripped of their dignity and good repute, their livelihoods, their homes and possessions, and even their children according to prejudicial laws and court processes that are feminist handiworks. These laws and processes favor plaintiffs, who are typically women, so their prejudices are favored by feminists. Feminists decry inequality when it’s non-advantageous. They’re otherwise cool with it. What’s more, when victims of the cause’s interests are women, those victims are just as indifferently shrugged off—as “casualties of war,” perhaps.
Women I’ve corresponded with in the three years I’ve maintained this blog have reported being stripped of their dignity and good repute, their livelihoods, their homes and possessions, and even their children according to prejudicial laws and court processes that are feminist handiworks. These laws and processes favor plaintiffs, who are typically women, so their prejudices are favored by feminists. Feminists decry inequality when it’s non-advantageous. They’re otherwise cool with it. What’s more, when victims of the cause’s interests are women, those victims are just as indifferently shrugged off—as “casualties of war,” perhaps. “
“ A false restraining order litigant with a malicious yen may leave a courthouse shortly after entering it having gained sole entitlement to a residence, attendant properties, and children, possibly while displacing blame from him- or herself for misconduct, and having enjoyed the reward of an authority figure’s undivided attention won at the expense of his or her victim.
A false restraining order litigant with a malicious yen may leave a courthouse shortly after entering it having gained sole entitlement to a residence, attendant properties, and children, possibly while displacing blame from him- or herself for misconduct, and having enjoyed the reward of an authority figure’s undivided attention won at the expense of his or her victim.
 “
“ The lawyers quoted by reporter, what’s more, refer to criminal cases in which sexual abuse is alleged and, consequently, in which the accused are afforded attorney representation.
The lawyers quoted by reporter, what’s more, refer to criminal cases in which sexual abuse is alleged and, consequently, in which the accused are afforded attorney representation.
 Faith in the conceit that restraining orders are minor impingements on defendants’ lives depends on accepting that being falsely, publically, and permanently labeled a stalker or batterer, for example, shouldn’t interfere with a person’s comfort, equanimity, or ability to realize his or her dreams. Such faith is founded, in other words, on the fantastical belief that wrongful vilification won’t exercise a detrimental influence on a person’s mental state, won’t affect his or her familial and social relationships, won’t negatively impact his or her employment and employability, etc.
Faith in the conceit that restraining orders are minor impingements on defendants’ lives depends on accepting that being falsely, publically, and permanently labeled a stalker or batterer, for example, shouldn’t interfere with a person’s comfort, equanimity, or ability to realize his or her dreams. Such faith is founded, in other words, on the fantastical belief that wrongful vilification won’t exercise a detrimental influence on a person’s mental state, won’t affect his or her familial and social relationships, won’t negatively impact his or her employment and employability, etc. As attorneys and
As attorneys and  A theme that emerges upon consideration of
A theme that emerges upon consideration of  It’s ironic that the focus of those who should be most sensitized to injustice is so narrow. Ironic, moreover, is that “emotional abuse” is frequently a component of state definitions of domestic violence. The state recognizes the harm of emotional violence done in the home but conveniently regards the same conduct as harmless when it uses the state as its instrument.
It’s ironic that the focus of those who should be most sensitized to injustice is so narrow. Ironic, moreover, is that “emotional abuse” is frequently a component of state definitions of domestic violence. The state recognizes the harm of emotional violence done in the home but conveniently regards the same conduct as harmless when it uses the state as its instrument. Here’s yet another irony. Too often the perspectives of those who decry injustices are partisan. Feminists themselves are liable to see only one side.
Here’s yet another irony. Too often the perspectives of those who decry injustices are partisan. Feminists themselves are liable to see only one side. Now consider the motives of false allegations and their certain and potential effects: isolation, termination of employment and impediment to or negation of employability, inaccessibility to children (who are used as leverage), and being forced to live on limited means (while possibly being required under threat of punishment to provide spousal and child support) and perhaps being left with no home to furnish or automobile to drive at all.
Now consider the motives of false allegations and their certain and potential effects: isolation, termination of employment and impediment to or negation of employability, inaccessibility to children (who are used as leverage), and being forced to live on limited means (while possibly being required under threat of punishment to provide spousal and child support) and perhaps being left with no home to furnish or automobile to drive at all.