Misperception of the significance of false accusations is a topic that’s been considered in past posts on this blog, particularly false accusations of sexual assault, which are the only false accusations anyone seems to believe are deserving of mention.
It’s wrong to say that the nature of false accusations doesn’t matter. But more relevant to observing corruption than a consideration of what is alleged is a consideration of how it’s alleged and decided.
Imagine if special courts were convened to judge accused people of a certain type, and imagine if the normal standards of evidence applied to allegations that may impute criminal wrongdoing to them were suspended. Imagine if instead of having to prove they had done what they were accused of, it were enough for a single judge (absent a jury) to “determine” upon a few minutes’ deliberation that the allegations were probably true and sufficiently urgent to merit the court’s intrusion.

These are among recent search terms that brought readers to this site.
If the accused people of a certain type were Jews or African-Americans, for instance, we would denounce these special courts to be an abomination. This kind of discrimination would raise our hackles.
Yet such special courts exist. Restraining order allegations are decided exactly this way, as may be allegations of domestic violence or rape, allegations that can also be made on restraining order petitions. There is nothing that can’t be alleged on a restraining order petition. Yet nothing alleged must be verified.
Now the critic of complaints about the harm of false allegations will chime in at this point and say, yeah, but it’s not like the victim of false accusations decided in a kangaroo court will be served a felony conviction.
Yes…and no. The critic should ask him- or herself what kind of person would maliciously or self-servingly lie about stalking, sexual violation, or violence and then ask him- or herself whether it’s reasonable not to expect more and worse from such a person.
Subsequent false allegations can give people criminal records (possibly, again, without a jury’s ever having vetted the evidence). They can give people criminal records because of the prior lie. A person can find him- or herself deprived of everything, including liberty, based on a tissue of frauds.
My ex-husband used to batter me and then go crawling on his hands and knees through the neighborhood until he reached the hospital or police station, and he would claim I had attacked him. I’d be hysterical, and police would arrest me. This happened repeatedly. […] I was made homeless on multiple occasions. He would involve my family, his family, all of our friends, employers, and university professors, and I was always the bad guy and still am. […] They filed restraining orders against me and claimed I was a danger to everyone; kidnapped my son, my dogs; stole my car at one point; drained bank accounts, PayPal accounts; and sawed locks of my storage unit and took off with everything…and EVERY F[—]ING TIME, police just validated the abuse and continued to terrorize me.
To complicate matters, a ruling on a false accusation can criminalize lawful behavior. So a subsequent allegation against someone can be true, but the alleged behavior that lands him or her in jail might only have been unlawful because of the original false accusation.
She filed a PFA [protection from abuse order] against me in April of 2014. Several months later, I was charged [by the district attorney on two counts of] violating the PFA. (1) My wife read my private password-protected Facebook emails. I asked a friend to contact her ex-husband #2 and tell him what was going on between her and me (he lives in Mexico and was listed on the PFA as one of the people I could not contact). The friend I emailed didn’t contact her ex-husband. In fact, nobody contacted her ex-husband. (2) I drafted a letter to my wife and gave it to my lawyer. My lawyer in turn forwarded it to her lawyer. They claimed this was also a PFA violation. We went to court, and the judge agreed on both counts and sent me to jail for 30 days. [This commenter’s wife was a Mexican national whom he met in March 2013 (Match.com) and married a month later. The PFA was filed after he “got her and her children their immigration papers” and later told her he wanted to divorce her because the marriage was unsatisfactory.]
Appreciate that one false record can be invoked until the end of time. The superficial critic thinks that once a trial is concluded and the framed victim survives his or her licks, the matter is concluded.
Not so. Ignoring the psychological residue for the moment, if the victim of a false accusation is falsely accused a second time, it can now be alleged that s/he has a “history” or “pattern” of abusive behavior, which may influence a divorce or child custody proceeding, a lawsuit, or even a criminal prosecution.
Respondent [—] and Father have a history of domestic violence that includes, but may not be limited to, the issuance of temporary restraining orders in cases […] and the issuance of a permanent restraining order in case […] which was entered by default on January 16, 2015, placing the welfare of the Child at risk. [The “Father” in this case was married to his wife for a brief period before she left and then filed a number of allegations of violence, both with the police and the court, over the ensuing six months. She then committed suicide after being institutionalized. She gave birth to a daughter a couple of months prior whom she had told the father she had miscarried. The father was never heard by a court in his defense but has nevertheless been represented as a serial abuser by the district prosecutor, who has sought to deny him any role in his child’s life.]
Lies that stick…cling, and they can be recycled. Public records don’t expire, and court rulings that impute grave misdeeds, even if those rulings were formed in mere minutes, aren’t questioned. They’re as valid as any other ruling.
Lies that stick, moreover, are entered into public (police) databases, registries that throw up red flags…indefinitely. The person falsely accused of domestic violence, for instance, may be permanently barred from certain types of employment and even, say, from attending his or her daughter’s dance recitals at school.
Defendant was refused jobs, [is] not allowed to attend [or] volunteer [at] her daughter’s school events, [and has had] numerous other rights taken away due to Plaintiff’s Abuse of Process and Fraudulent Allegations and written Affidavit to the Court. This continues today. [This is an excerpt from the draft of a commenter’s “Motion to Expunge,” which she was preparing herself with no legal know-how.]
Again, privations endure permanently, for always, ad infinitum.
The liberal critic who declaims s/he’s for immigrant rights and for restraining orders should be aware that a non-citizen who’s falsely accused in a restraining order proceeding and then accused of violating an order obtained by fraud can be summarily booted from the country: Adios, muchachito (we don’t like your kind here).
Based on lies, people are deprived of their good names, their dignity, their children, their homes, their property, their livelihoods, and their security.
Finally, being lied about and then scorned by cops and lambasted by judges—these traumas last, and they last no less indefinitely than false records do. So on top of everything else, people may be driven out of their minds.
Copyright © 2015 RestrainingOrderAbuse.com
*Public records, besides being permanent, are also public records, and a lie that a judge legitimates is a lie that everyone else will regard as true (e.g., a neighbor, a boy- or girlfriend, a student, a patient, a client, an employer, a loan officer, a landlord….).
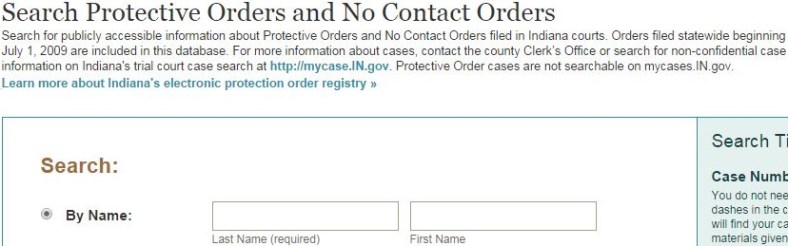
 One of the thrusts of the Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) has been to establish public restraining order registries like those that identify sex offenders.
One of the thrusts of the Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) has been to establish public restraining order registries like those that identify sex offenders.